Search Criteria
A SearchCriteria object defines the filtering logic for API search operations. It determines which records to include or exclude from your result set, functioning similarly to a WHERE clause in SQL.
Overview
Search criteria allow you to filter data based on specific conditions. Each criteria definition consists of one or more filter conditions that can be combined using logical operators (AND/OR) and parenthetical grouping to create precise data queries.
Structure of a SearchCriteria Object
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
searchConfigId |
string | Identifies which search configuration to use (e.g., "CLAIMBATCH", "CLAIM") |
criteria_Key |
number | Unique identifier for saved criteria (system-generated for persistent criteria) |
description |
string | Human-readable description of the criteria's purpose |
temporary |
boolean | When true, criteria is stored temporarily; when false, it's persisted |
criteriaDetails |
array | Collection of individual filter condition objects |
Filter Condition Properties
Each object in the criteriaDetails array defines a single filter condition:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
criteria_Table |
string | Database table containing the field to filter |
criteria_Column |
string | Column/field name to apply the filter to |
criteria_Data_Type |
string | Data type ("string", "number", "date", etc.) |
criteria_Operator |
string | Comparison operator ("=", ">", "<", "LIKE", "BETWEEN", etc.) |
criteria_From_Value |
string | Primary comparison value (all values are sent as strings) |
criteria_To_Value |
string | Optional upper bound for range operations like "BETWEEN" |
criteria_Join |
string | Logical operator ("AND", "OR") connecting to the next condition |
criteria_Group |
number | Groups conditions with parentheses (same number = same group) |
Visual Representation
Basic Single Condition
A simple filter using one condition:
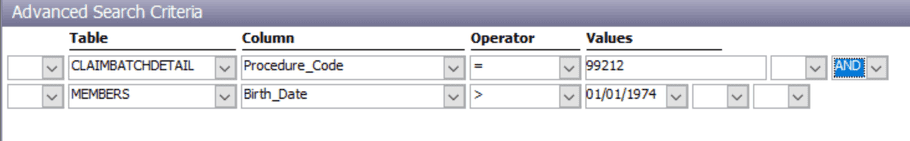
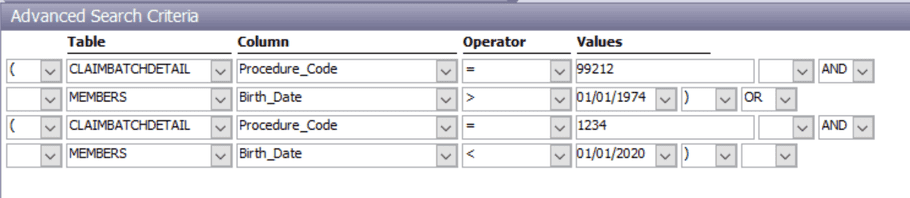
Advanced Multiple Conditions
Complex filtering with logical grouping:
JSON Examples
Single Condition Example
{
"searchConfigId": "CLAIMBATCH",
"criteria_Key": 84,
"description": "Claim Batches with Proc Code 99212",
"temporary": false,
"criteriaDetails": [
{
"criteria_Table": "CLAIMBATCHDETAIL",
"criteria_Column": "Procedure_Code",
"criteria_Data_Type": "string",
"criteria_Operator": "=",
"criteria_From_Value": "99212"
}
]
}Multiple Conditions Example
{
"searchConfigId": "CLAIM",
"criteria_Key": 92,
"description": "High Value Claims from Last Month",
"temporary": true,
"criteriaDetails": [
{
"criteria_Table": "CLAIM",
"criteria_Column": "Claim_Amount",
"criteria_Data_Type": "number",
"criteria_Operator": ">",
"criteria_From_Value": "5000",
"criteria_Join": "AND"
},
{
"criteria_Table": "CLAIM",
"criteria_Column": "Claim_Date",
"criteria_Data_Type": "date",
"criteria_Operator": "BETWEEN",
"criteria_From_Value": "2023-01-01",
"criteria_To_Value": "2023-01-31"
}
]
}Implementation Best Practices
Transient vs. Persistent Criteria
For One-Time Searches
Use "In Memory" criteria when executing one-time or ad-hoc searches. This approach prevents unnecessary storage in the CriteriaTable, reducing database overhead.
For Temporary Use (temporary: true)
- Criteria are stored transiently in the system
- Each SearchConfig maintains the five most recent temporary criteria for quick reuse
- Ideal for criteria you may need again in the short term but don't need permanently
For Long-Term Use (temporary: false)
- Criteria are persisted indefinitely in the database
-
Recommended for:
- Frequently used search patterns
- User-defined filters
- Report templates
- Common query definitions
Performance Optimization
- Minimize conditions : Include only necessary filter conditions
- Leverage indexed columns : Prioritize filtering on indexed fields when possible
- Break down complex queries : For intricate search needs, consider multiple smaller, targeted criteria
- Order conditions efficiently : Place the most restrictive conditions first when filtering large datasets